Dental Implants
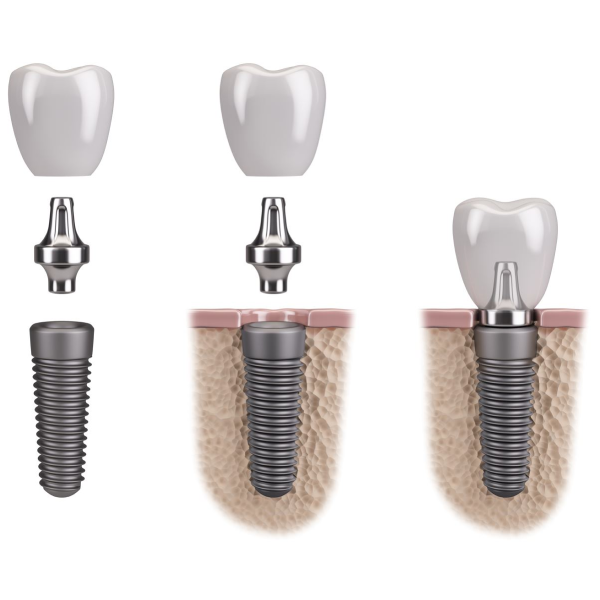
A dental implants is a surgical component inserted into the jaw bone to hold a replacement tooth, bridge, or denture. They are an excellent option for replacing one or more missing teeth. They can also be used to support loose dentures.
Dental implants are usually made of medical-grade titanium.
Procedure
It is a two-step procedure: implant insertion, followed by restoration of the implant with a crown. It is a team effort between your surgeon and your dentist. The procedure may need to be performed under a general anesthetic if there are multiple implants, or if extensive surgery is required.
Implant insertion involves making a cut in the gum, drilling a hole in the bone, and screwing in the dental implant. The dental implant is left to fuse with the bone. This is a process called osseointegration. The second step is often performed by the dentist, which is the fitting of the crown (replica tooth). For dentures, the second step is fitting the denture to the implants.
If there is an inadequate amount of bone to receive the implant, your surgeon may need to perform a bone graft by taking bone from another part of the mouth or using a bone substitute.
Downtime
The amount of downtime required after placement of a dental implant depends on the number of implants and the amount of surgery required. Taking the rest of the day off work or school is all that may be required after placing a single implant. Up to a week may be required if multiple implants have been placed or if extensive surgery has been required. Your surgeon will be able to advise you on the amount of time needed off work. During this time a soft diet is advised in addition to avoidance of alcohol and cigarette smoking.
Potential risks of Dental Implants
Despite the highest standard of care by your surgeon, there are always risks associated with dental implant surgery. Some risks include:
- Pain and discomfort;
- Failure of osseointegration;
- Loosening of the implant;
- Infection;
- Swelling;
- Excessive bleeding;
- Limited mouth opening;
- Damage to adjacent teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions
A dental implant is a surgical component that is inserted into the jaw bone to hold a replacement tooth, bridge, or denture. They are an excellent option for replacing one or more missing teeth. They can also be used to support loose dentures.
Dental implants are usually made of medical-grade titanium.
Despite the highest standard of care by your surgeon, there are always risks associated with dental implant surgery. Some risks include:
- Pain and discomfort;
- Failure of osseointegration (rejection of the implant);
- Loosening of the implant;
- Infection;
- Swelling;
- Excessive bleeding;
- Limited mouth opening;
- Damage to adjacent teeth.